product description
Basic Info.
N-Ethylaniline Properties
| Melting point | -63 °C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 205 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.963 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 4.2 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.2 mm Hg ( 25 °C) |
| refractive index | n20/D 1.554(lit.) |
| Flash point | 185 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 2.7g/l |
| pka | 5.12(at 24℃) |
| form | Liquid |
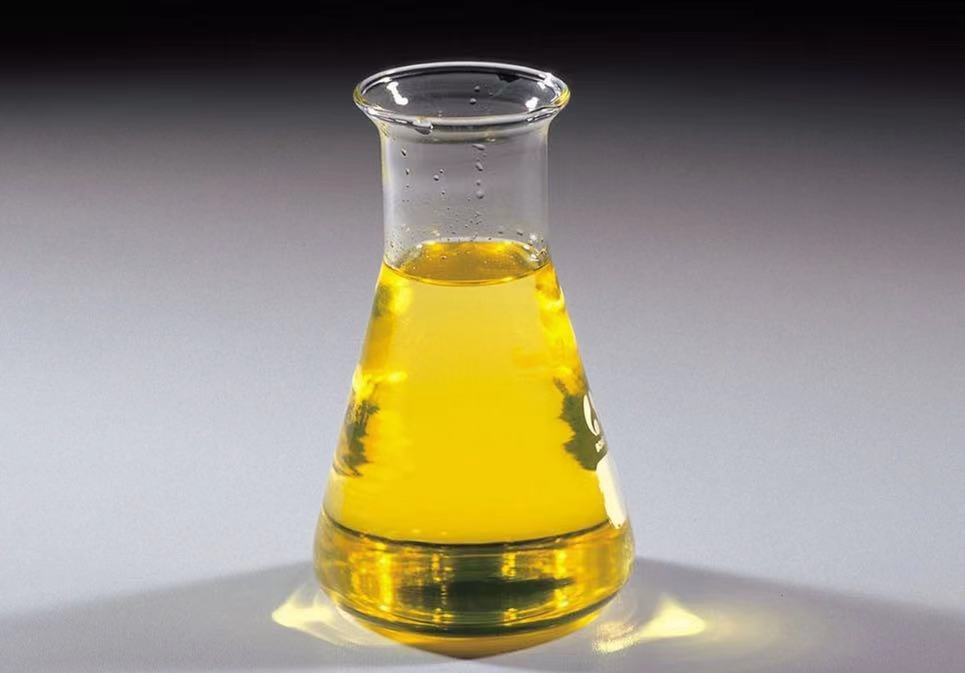
| color | Clear light yellow to light brown |
| PH | 11 (2.7g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| explosive limit | 1.8-10.0%(V) |
| Water Solubility | 50 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Air & Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,3764 |
| BRN | 507468 |
| Dielectric constant | 5.9(20℃) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH: IDLH 100 ppm |
| Stability | Stable, but decomposes upon prolonged exposure to air or light. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. May react violently with nitric acid. |
| InChI | 1S/C8H11N/c1-2-9-8-6-4-3-5-7-8/h3-7,9H,2H2,1H3 |
| InChIKey | OJGMBLNIHDZDGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
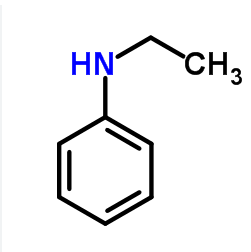
| SMILES | CCNc1ccccc1 |
| LogP | 2.26 at 25℃ and pH6-8 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 103-69-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EWG’s Food Scores | 1 |
| FDA UNII | 7E45L4I2PS |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzenamine, N-ethyl-(103-69-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | N-Ethylaniline (103-69-5) |
| UNSPSC Code | 12352100 |
| NACRES | NA.22 |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS06,GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H301+H311+H331-H373 |
| Precautionary statements | P260-P280-P301+P310-P302+P352+P312-P304+P340+P311-P314 |
| PPE | Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | T |
| Risk Statements | 23/24/25-33 |
| Safety Statements | 28-37-45-28A |
| RIDADR | UN 2272 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | BX9780000 |
| F | 8 |
| Hazard Note | Toxic |
| TSCA | TSCA listed |
| HazardClass | 6.1 |
| PackingGroup | III |
| HS Code | 29214200 |
| Storage Class | 6.1C – Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects |
| Hazard Classifications | Acute Tox. 3 Dermal Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation Acute Tox. 3 Oral STOT RE 2 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 103-69-5(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LD50 in rats (g/kg): 0.18 i.p., 0.28 orally, 4.7 s.c. (Sziza, Podhragyai) |
N-Ethylaniline Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
N-Ethylaniline is a yellow brown oil with aweak fishy odor. Molecular weight = 121.20; Boilingpoint = 205℃; Freezing/Melting point = -64℃; Flashpoint = 85℃ (oc). Flammable Limits: LEL 1.6%; UEL9.5%. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 M RatingSystem): Health 3, Flammability 2, Reactivity 0. Insolublein water.
Chemical Properties
yellow liquid
Chemical Properties
N-Ethylaniline is yellow-brown oil with a weak fishy odor.
Occurrence
Polyethylene bottles used in intravenous solutions have been reported to be contaminated with N-ethylaniline from rubber parts of the closure (Ulsaker and Teien 1979). It has been reported that rubber containing N,N,-dithiodimorpholine accelerator of vulcanization can release N-ethylaniline into an aqueous media (Stankevich and Shurupova 1976). This compound has also been reported as a contaminant of cigarette smoke at a level of 55.8 ng per one U.S. 85 mm cigarette (Patrianakos and Hoffmann 1979).
Uses
N-Ethylaniline is used as an explosive stabilizer and in dyestuff manufacture.
Uses
Organic synthesis.
Uses
N-Ethylaniline (NEA) may be used as an internal standard in the GC analysis of nicotine extraction from nicotine gum. It may be used in the synthesis of the following, 2-(N-ethylphenylamino)-1,4-benzoquinone, 2-(arylaminomethyl)phenylboronic acid, poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) films containing NEA and poly(N-ethylaniline) (PNEA).
Definition
ChEBI: N-Ethylaniline is a member of benzenes.
Production Methods
Manufacture of N-ethylaniline is based on the reaction of aniline with alkyl halide or by heating aniline with ethyl alcohol under acidic conditions followed by purification (Windholz et al 1983).
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 78, p. 4778, 1956 DOI: 10.1021/ja01599a063
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 21, p. 988, 1956
Tetrahedron Letters, 25, p. 1635, 1984 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)81131-X
General Description
A dark liquid with an aromatic odor. Insoluble in water. Density 0.963 g / cm3. Toxic by skin absorption and inhalation of vapors. Evolves toxic fumes during combustion. Flash point 185°F.
Air & Water Reactions
Unstable to prolonged exposure to air and/or light. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
N-Ethylaniline may react violently with nitric acid. May react with strong oxidizing agents. . Neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen may be generated in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Health Hazard
N-Ethylaniline is considered very hazardous in a fire situation, since it is highly toxic and readily absorbed by the inhalation, dermal and oral routes (HSDB 1988). Excessive exposure causes respiratory paralysis.
Fire Hazard
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form.
Industrial uses
N-Ethylaniline is used as an explosives stabilizer and as an intermediate in the manufacturing of dyes and pharmaceuticals (Northcott 1978).
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by an unspecified route. Mddly toxic by skin contact. An allergen. Flammable when exposed to heat or flame; can react with oxidizing materials. To fight fire, use dry chemical, CO2, foam. Hypergolic reaction with red fuming nitric acid. When heated to decomposition or on contact with acid or acid fumes it emits highly toxic fumes of aniline and NOx.
Potential Exposure
This material is used as an intermediate in dyes, pharmaceuticals and explosives; in organic synthesis.
First aid
Eye Contact: Immediately remove any contactlenses and flush with large amounts of water for at least 15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention if any symptoms are present.Skin Contact: Quickly remove contaminated clothing.Immediately wash area with large amounts of soap,promptly seek medical attention.Breathing: Remove the person from exposure. Begin rescuebreathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR if heart actionhas stopped. Transfer promptly to a medical facility.Note to physician: Treat for methemoglobinemia.Spectrophotometry may be required for precise determination of levels of methemoglobinemia in urine.
Metabolism
The metabolism of N-ethylaniline has been studied more as a tool to understanding microsomal drug metabolizing activity than as the central item of inquiry. However, the following have been clearly defined as metabolic products of N-ethylaniline: phenylhydroxylamine, N-hydroxyl, N-ethylaniline; N-ethyl-p-aminophenol; and aniline (Appel et al 1965; Heinze 1970; Hlavica 1970; Hlavica and Kiese 1969; Kampffmeyer and Kiese 1965; Kroeber et al 1970; Lange 1967 and Lange 1968). Nonmicrosomal metabolism has not been reported. Species shown capable of metabolism include rabbit, mouse, rat, dog, pig, and guinea pig with the proportions of the various metabolites often species dependent. Compounds similar to N-ethylaniline such as N-methyl-N-ethylaniline can form N-ethylaniline via demethylation (Gorrod et al 1975a,b).
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Ethylaniline must be stored to avoid contact withstrong acids (such as hydrochloric, sulfuric, and nitric) andstrong oxidizers since violent reactions occur. Store intightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area.Sources of ignition, such as smoking and open flames, areprohibited where ethylaniline is used, handled, or stored ina manner that could create a potential fire or explosionhazard.
Shipping
UN2272 N-Ethylaniline, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials
Incompatibilities
May form explosive mixture with air. Decomposes on contact with light or air. Reacts with many materials. Neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. Flammable gaseous hydrogen may be generated in combination with strong reducing agents such as hydrides, nitrides, alkali metals, and sulfides. Contact with strong oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials; strong acids, such as nitric acid, can cause fire; explosions with formation of toxic vapors of aniline and oxides of nitrogen; strong bases, isocyanates, halogenated organics, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides
N-Ethylaniline Preparation Products And Raw materials
FAQ
Q1: About the after-sale service of products
A: After purchasing the products from our factory, we have A professional technical team and after-sales team to serve you and solve all your problems in the future.
Q2: Can I get some samples?
A: Yes, we can provide samples, but the customer will pay the freight.
Q3: How do I start paying?
Payment can be made by wire transfer or T/T, apple_pay, google_pay, gc_real_time_bank_transfer , etc.
Q4: How to confirm product quality before placing an order?
A: You can get free samples of some products. You just have to pay the shipping fee or arrange for the sample to be sent to us by express.
You can send us your product specifications and requirements and we will produce products according to your requirements.
Q5: What is your MOQ?
A: The minimum quantity we can order is 1kg.
But usually we can accept a smaller quantity, say 100g, at the cost of 100% sample charge.
Q6: Shipping Time?
A: We ship the parcel out in 1-2 days and offer tracking No.. Shipping time is different to different country. Please consult
| ACF Chemical Co., Ltd.
Leon phone/whatsapp:008615950692266 email:md@acfchemical.com No. 45 Pengwan Road, Qianwan Bonded Port Area, Qingdao Area, China (Shandong) |
|
| DMEA | 108-01-0 |
| Dodecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride | 112-00-5 |
| N-Hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride | 112-02-7 |
| 1831 | 112-03-8 |
| 1631Br | 57-09-0 |
| D821 | 5538-94-3 |
| D8/1021 | 68424-95-3 |
| D1021 | 7173-51-5 |
| D1821 | 61789-80-8 |
| TEP88 | 157905-74-3 |
| 1227 C12 | 139-07-1 |
| DMPT(N,N-Dimethyl-p-toluidine) | 99-97-8 |
| NDPT(N,N-dihydroxyethyl-p-toluidine) | 3077-12-1. |
| DMA(N,N-dimethylaniline) | 121-69-7 |
| N,N-Diethylaniline | 91-66-7 |
| MT(M-Toluidine) | 108-44-1 |
| PT(P-Toluidine) | 106-49-0 |
| O-Toluidine OT | 95-53-4 |
| Dimethyl(octyl)amine | 7378-99-6/1120-24-7 |
| C16-18-alkyldimethyl Octadecyl/Hexadecyl dimethylamines | 68390-97-6 |
| Octadecyl/behenyl dimethylamines | 124046-42-0 |
| N,N-dimethyldocosylamine | 21542-96-1 |
| N-Methyldioctylamine | 4455-26-9 |
| Di(octyl/decyl) methylamines | 308062-61-5 |
| Didecyl methylamine | 7396-58-9 |
| N-methyldidodecylamine | 2915-90-4 |
| Dipalmitamine | 16724-61-1 |
| Trioctylamine | 1116-76-3 |
| Trioctylamine | 68814-95-9 |
| N-3-Laurylamidopropyl dimethylamine | 3179-80-4 |
| N-3-(Hydrogenated cocoamido)propyl dimethylamines | 288095-05-6 |
| N-3-Oleylamidopropyl dimethylamine | 109-28-4 |
| N-3-Erucylamidopropyl dimethylamine | 60270-33-9 |
| N-Oleyl 1,3-propanediamine | 7173-62-8 |
| Bis(aminopropyl)laurylamine | 2372-82-9 |
| N-tallow alkyltripropylenetetra | 68911-79-5 |
| 3-(isodecyloxy)propylamine | 30113-45-2 |
| N-[3-(isodecyloxy)propyl]propane-1,3-diamine | 72162-46-0 |
| 2-(Methylamino)ethanol | 109-83-1 |
| N-Methyldiethanolamine | 105-59-9 |
| 3-Methoxy propyl amine | 5332-73-0 |
| N,N-dimethylcyclohexylamine | 98-94-2 |
| 1,3,5-Tris[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]hexahydro-1,3,5-triazine | 15875-13-5 |
| N,N,N’-trimethylamino-N’-ethylethanolamine | 2212-32-0 |
| N,N-Dimethylethanolamine | 108-01-1 |
| Acetone | |
| Acrylic acid | |
| Adipic acid | |
| Alpha-Methylstyrene (AMS) | |
| Benzoic Acid | |
| Bisphenol A | |
| Butyl Acrylat (BA) | |
| Butyl acetate (Butac) | |
| Butyl diglycol (BDG) | |
| Butyl glycol | |
| Para-tertiary butyl benzoic acid (PTBBA) | |
| n-Butanol | |
| n-Butyl methacrylate (n-BUMA) | |
| para-tert. Butylphenol (PTBP) | |