Introducing several types of epoxy curing agents.
Epoxy resin cured products are widely used as resin matrices in advanced composite materials. The different cross-linked network structures formed by the curing reaction of different curing agents with epoxy resins result in different properties, directly affecting the thermal characteristics of the epoxy resin. Among the various types of epoxy resins, bisphenol A diglycidyl ether epoxy resin is the most widely used and has the largest production volume. Its chemical structure is shown in the figure.
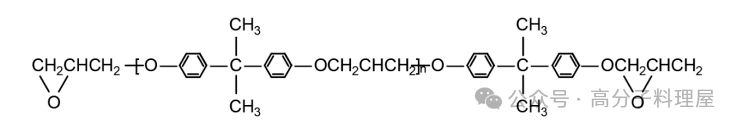
The macromolecular structure of bisphenol A epoxy resin has the following characteristics: (1) The ends of the macromolecule are highly reactive epoxy groups; (2) The main molecular chain contains many ether linkages, forming a linear polyether structure; (3) Resins with a large N value have many secondary hydroxyl groups appearing regularly and far apart; (4) There are also a large number of benzene rings, methylene groups, and isopropyl groups. The epoxy and hydroxyl groups are the main curing reaction groups, providing the epoxy resin with cohesive strength and adhesive strength; the ether linkages and hydroxyl groups are polar groups, which improve the wettability and adhesion of the resin; the ether linkages and C-C bonds give the epoxy resin molecule flexibility; the benzene rings give the polymer a certain degree of heat resistance and rigidity; the high bond energy of the C-O bond makes the epoxy resin resistant to alkalis.
Diethylenetriamine (DETA)
DETA belongs to the class of fatty amine curing agents. It is characterized by low viscosity and can cure epoxy resins at room temperature, but it has a short pot life. The molecular structure of diethylenetriamine is:
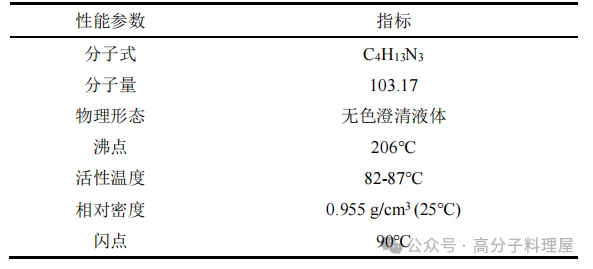
m-Xylylenediamine (m-XDA)
m-XDA is an aromatic amine curing agent that cures at room temperature, has a long pot life, and exhibits good heat resistance, but it is prone to absorbing CO2 from the air, leading to bubble formation. The molecular structure of m-xylylenediamine is:
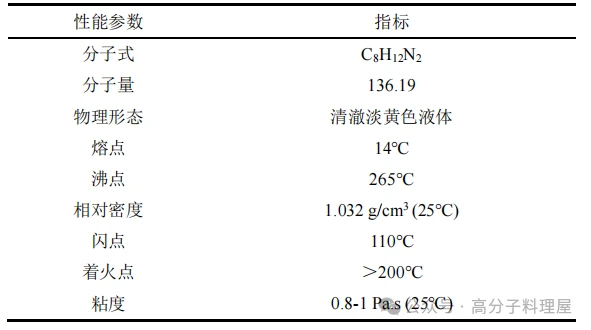
Low molecular weight polyamide 650 (PA650)
PA650 is a polyamide-polyamine curing agent with a wide range of mixing ratios with epoxy resins, offering balanced mechanical properties, good adhesion, and excellent thermal shock resistance. Its molecular structure is as follows:
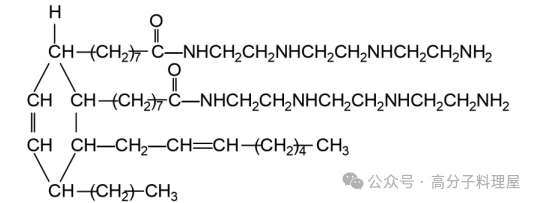
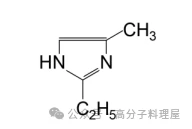
2-ethyl-4-methylimidazole (2E4MZ)
2E4MZ is an imidazole-based curing agent that requires a small amount for effective curing of epoxy resins. It has a long pot life at room temperature and can be cured at moderate temperatures (80-120°C). The cured product exhibits high mechanical strength and good heat resistance, but its chemical resistance and water resistance are inferior to those of aromatic amine-based cured products. Its molecular structure is as follows: