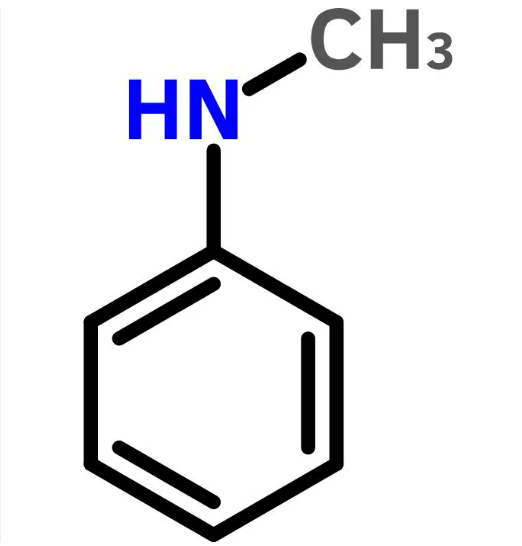
product description
Basic Info.
N-Methylaniline Properties
| Melting point | -57 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 196 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.989 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0.5 hPa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | n20/D 1.571(lit.) |
| Flash point | 174 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | water: slightly soluble30g/L |
| pka | 4.84(at 25℃) |
| form | Liquid |
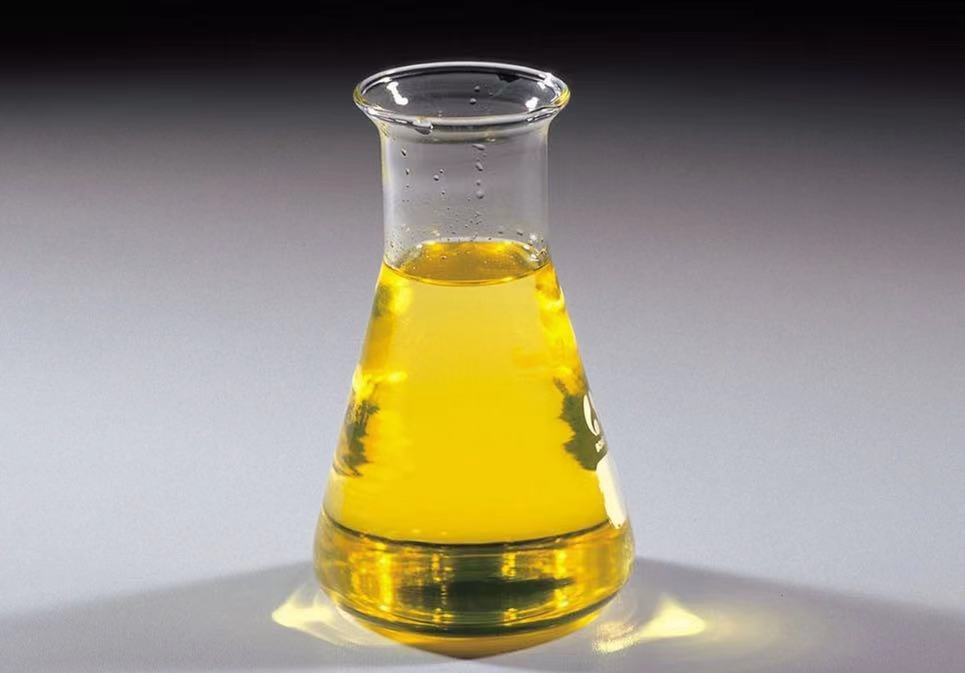
| color | Clear yellow to brown |
| Odor | Moderate aniline-type. |
| PH | 7.6 (1g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 30 g/L |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,6019 |
| BRN | 741982 |
| Henry’s Law Constant | (x 10-5 atm?m3/mol): 1.19 at 25 °C (approximate – calculated from water solubility and vapor pressure) |
| Dielectric constant | 6.0(22℃) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 0.5 ppm (2 mg/m3), IDLH 100 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA 2 ppm (9 mg/m3); ACGIH TLV: TWA 0.5 ppm (adopted). |
| Stability | Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Discolours upon exposure to air. |
| InChI | 1S/C7H9N/c1-8-7-5-3-2-4-6-7/h2-6,8H,1H3 |
| InChIKey | AFBPFSWMIHJQDM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CNc1ccccc1 |
| LogP | 1.66 at 20℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 100-61-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EWG’s Food Scores | 1 |
| FDA UNII | TH45GK410O |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Aniline, N-methyl-(100-61-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | N-Methylaniline (100-61-8) |
| UNSPSC Code | 41116107 |
| NACRES | NA.24 |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS06,GHS08,GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H301+H311+H331-H319-H373-H410 |
| Precautionary statements | P273-P280-P301+P310-P302+P352+P312-P304+P340+P311-P314 |
| target organs | Liver,spleen,Bone marrow |
| PPE | Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | T,N |
| Risk Statements | 23/24/25-33-50/53 |
| Safety Statements | 28-36/37-45-60-61-28A |
| RIDADR | UN 2294 6.1/PG 3 |
| OEB | B |
| OEL | TWA: 0.5 ppm (2 mg/m3) [skin] |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | BY4550000 |
| F | 8 |
| Autoignition Temperature | 500 °C |
| TSCA | TSCA listed |
| HazardClass | 6.1 |
| PackingGroup | III |
| HS Code | 29214200 |
| Storage Class | 6.1C – Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects |
| Hazard Classifications | Acute Tox. 3 Dermal Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation Acute Tox. 3 Oral Aquatic Acute 1 Aquatic Chronic 1 Eye Irrit. 2 STOT RE 2 Oral |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 100-61-8(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LD in rabbits (g/kg): 0.28 orally; in rabbits, cats (mg/kg): 24, 24 i.v. (Treon) |
| IDLA | 100 ppm |
| Limited Quantities | 5.0 L (1.3 gallons) (liquid) or 5.0 kg (11 lbs) (solid) |
| Excepted Quantities | Max Inner Pack (30g or 30ml) and Max Outer Pack (1Kg or 1L) |
N-Methylaniline Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
N-Methylaniline is a yellow to light brown oily liquid with a weak, ammonia-like odor. Turns reddishbrown if left standing. The odor threshold is 1.7 ppm. Molecular weight= 107.17; Specific gravity (H2O:1)= 0.99;Boiling point=195.6℃; Freezing/Melting point=57.2℃; Vapor pressure= 0.3 mmHg at 20℃; Flash point=79.4℃. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 2, Flammability 2, Reactivity 0. Practically insoluble in water.
Chemical Properties
N-Methylaniline is a yellow to light brown oily liquid with a weak, ammonia-like odor. soluble in ethanol, ether, chloroform, slightly soluble in water. Turns reddishbrown if left standing.
Physical properties
Colorless to yellow to pale brown liquid with a faint, ammonia-like odor. Odor threshold concentration is 1.7 ppm (quoted, Amoore and Hautala, 1983).
Uses
N-Methylaniline is used as a solvent and in organic synthesis. It is used in the production of cationic brilliant red FG, cationic pink B, reactive yellow brown KGR, etc. in the dye industry. N-methylaniline is an intermediate in the synthesis of the insecticide buprofezin and the herbicide mefenacet.
Uses
N-methylaniline was used as raw material, and metal-organic skeleton material CAU-10pydc was used as catalyst to catalyze the reaction of CO2 with n-methylaniline to produce N-methyl-N-phenylformamide in mild conditions and green solvent acetonitrile[1]. Poly (N-methylaniline) (PNMA) was prepared by the electrooxidation of N-methylaniline in acidic aqueous solution. PNMA prepared in acidic aqueous solution with different organic solvents and anions had different conductivity. Such as the experimental group added acetonitrile, N, N-dimethylformamide and dimethylsulfoxide, and the experimental group which adding dimethylsulfoxide had the strongest conductivity[2].
References:
[1] Zhiqiang Wang, Chenghua Deng, Xiao Liu, Wenmin Wang, Highly efficient conversion of CO2 into N-formamides catalyzed by a noble-metal-free aluminum-based MOF under mild conditions, 2023, 52, 11163-11167.
[2] Jun YANO , Hiroko YOSHIKAWA , Tomomi MUKAI , Sumio YAMASAKI , Akira KITANI, Effect of Anions and Added Organic Solvents of Polymerizing Solutions on the Conductivity of Poly (N-methylaniline), 2006, 74, 42-48.
Preparation
N-methylaniline was synthesized by the reaction of aniline with dimethyl sulfate. Dimethyl sulfate was added dropwise to the mixed solution of aniline and water below 10°C, stirred for 1 h, and then added dropwise with 30% sodium hydroxide solution. The upper layer is the organic phase, and the lower layer is extracted with benzene. After the benzene is recovered from the extract, the obtained oil Chemicalbook-like substance is combined with the organic phase to obtain a mixture of aniline, N-methylaniline and N,N-dimethylaniline. The mixture was treated with sulfuric acid, and the aniline formed sulfate crystals which were filtered off. N,N-dimethylaniline can be converted to N-methylaniline by the following reaction.
Application
N-Methylaniline (NMA) was used in the preparation of self-assembled poly(N-methylaniline)-lignosulfonate (PNMA-LS) composite spheres with reactive silver-ion adsorbability. NMA was also used in electrodeposition of poly(N-methylaniline) (PNMA) coatings on a steel disc electrode using potentiodynamic, potentiostatic and galvanostatic techniques.
Definition
ChEBI: N-methylaniline is a methylaniline that is aniline carrying a methyl substituent at the nitrogen atom. It is a phenylalkylamine, a secondary amine and a methylaniline. It derives from an aniline.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 14, p. 1007, 1966 DOI: 10.1248/cpb.14.1007
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 107, p. 493, 1985 DOI: 10.1021/ja00288a037
Synthetic Communications, 13, p. 601, 1983 DOI: 10.1080/00397918308059535
General Description
Chemical oxidation of N-methylaniline with dichromate (oxidant) has been studied by Raman spectroscopy.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and skin absorption. Methemoglobinemia and central nervous system impairment.
Health Hazard
Recommended Personal Protective Equipment: Approved respirator; rubber gloves; splash proof goggles; Symptoms Following Exposure: Inhalation causes dizziness and headache. Ingestion causes bluish discoloration (cyanosis) of lips, ear lobes, and fingernail beds. Liquid irritates eyes. Absorption through skin produces same symptoms as for ingestion; General Treatment for Exposure: INHALATION: remove victim to fresh air and call a physician at once; administer oxygen until physician arrives. INGESTION: give large amount of water; get medical attention at once. EYES or SKIN: flush with plenty of water for at least 15 min.; if cyanosis is present, shower with soap and warm water, with special attention to scalp and finger nails; remove any contaminated clothing; Toxicity by Inhalation (Threshold Limit Value): Data not available; Short-Term Inhalation Limits: Data not available; Toxicity by Ingestion: Data not available; Late Toxicity: Data not available; Vapor (Gas) Irritant Characteristics: Data not available; Liquid or Solid Irritant Characteristics: Data not available; Odor Threshold: Data not available.
Chemical Reactivity
Reactivity with Water No reaction; Reactivity with Common Materials: May attack some forms of plastic; Stability During Transport: Stable; Neutralizing Agents for Acids and Caustics: Not pertinent; Polymerization: Not pertinent; Inhibitor of Polymerization: Not pertinent.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intravenous routes. Moderately toxic by subcutaneous route. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Potential Exposure
The material is used as an intermediate in organic synthesis, as a solvent and as an acid acceptor
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove any contact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least 15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts the skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medical facility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit. Medical observation is recommended for 2448 h after breathing overexposure, as pulmonary edema may be delayed. As first aid for pulmonary edema, a doctor or authorized paramedic may consider administering a corticosteroid spray. Note to physician: Treat for methemoglobinemia. Spectrophotometry may be required for precise determination of levels of methemoglobin in urine.
Carcinogenicity
N-methyl aniline (1.95 g/kg of food) given together with sodium nitrite (1.0 g/l of drinking water) to Swiss mice resulted in a 17% incidence of lung adenomas and a 14% incidence of malignant lymphomas; there were no carcinogenic effects in animals treated with Nmethyl aniline alone, suggesting that in vivo nitrosation is necessary for forming carcinogenic nitrosamines.
In bacterial mutagenicity assays N-methyl aniline was negative with or without metabolic activation.
Environmental Fate
Soil. Reacts slowly with humic acids or humates forming quinoidal structures (Parris, 1980).
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Store in a secure poison location. Prior to working with this chemical you should be trained on its proper handling and storage. Methylaniline must be stored to avoid contact with strong acids (such as hydrochloric, sulfuric, and nitric), since violent reactions occur. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area away from heat. Sources of ignition, such as smoking and open flames, are prohibited where methylaniline is used, handled, or stored in a manner that could create a potential fire or explosion hazard.
Shipping
UN2294 N-Methylaniline, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Purification Methods
Dry it with KOH pellets and fractionally distil it under vacuum. Acetylate, and the acetyl derivative is recrystallised to constant melting point (m 101-102o), then hydrolysed with aqueous HCl and distilled from zinc dust under reduced pressure. [Hammond & Parks J Am Chem Soc 77 340 1955, Beilstein 12 IV 241.]
Incompatibilities
Reacts violently with strong acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, strong oxidizers. Attacks some plasti℃.
Waste Disposal
Controlled incineration whereby oxides of nitrogen are removed from the effluent gas by scrubber, catalytic or thermal device.
N-Methylaniline Preparation Products And Raw materials
FAQ
Q1: About the after-sale service of products
A: After purchasing the products from our factory, we have A professional technical team and after-sales team to serve you and solve all your problems in the future.
Q2: Can I get some samples?
A: Yes, we can provide samples, but the customer will pay the freight.
Q3: How do I start paying?
Payment can be made by wire transfer or T/T, apple_pay, google_pay, gc_real_time_bank_transfer , etc.
Q4: How to confirm product quality before placing an order?
A: You can get free samples of some products. You just have to pay the shipping fee or arrange for the sample to be sent to us by express.
You can send us your product specifications and requirements and we will produce products according to your requirements.
Q5: What is your MOQ?
A: The minimum quantity we can order is 1kg.
But usually we can accept a smaller quantity, say 100g, at the cost of 100% sample charge.
Q6: Shipping Time?
A: We ship the parcel out in 1-2 days and offer tracking No.. Shipping time is different to different country. Please consult
| ACF Chemical Co., Ltd.
Leon phone/whatsapp:008615950692266 email:md@acfchemical.com No. 45 Pengwan Road, Qianwan Bonded Port Area, Qingdao Area, China (Shandong) |
|
| DMEA | 108-01-0 |
| Dodecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride | 112-00-5 |
| N-Hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride | 112-02-7 |
| 1831 | 112-03-8 |
| 1631Br | 57-09-0 |
| D821 | 5538-94-3 |
| D8/1021 | 68424-95-3 |
| D1021 | 7173-51-5 |
| D1821 | 61789-80-8 |
| TEP88 | 157905-74-3 |
| 1227 C12 | 139-07-1 |
| DMPT(N,N-Dimethyl-p-toluidine) | 99-97-8 |
| NDPT(N,N-dihydroxyethyl-p-toluidine) | 3077-12-1. |
| DMA(N,N-dimethylaniline) | 121-69-7 |
| N,N-Diethylaniline | 91-66-7 |
| MT(M-Toluidine) | 108-44-1 |
| PT(P-Toluidine) | 106-49-0 |
| O-Toluidine OT | 95-53-4 |
| Dimethyl(octyl)amine | 7378-99-6/1120-24-7 |
| C16-18-alkyldimethyl Octadecyl/Hexadecyl dimethylamines | 68390-97-6 |
| Octadecyl/behenyl dimethylamines | 124046-42-0 |
| N,N-dimethyldocosylamine | 21542-96-1 |
| N-Methyldioctylamine | 4455-26-9 |
| Di(octyl/decyl) methylamines | 308062-61-5 |
| Didecyl methylamine | 7396-58-9 |
| N-methyldidodecylamine | 2915-90-4 |
| Dipalmitamine | 16724-61-1 |
| Trioctylamine | 1116-76-3 |
| Trioctylamine | 68814-95-9 |
| N-3-Laurylamidopropyl dimethylamine | 3179-80-4 |
| N-3-(Hydrogenated cocoamido)propyl dimethylamines | 288095-05-6 |
| N-3-Oleylamidopropyl dimethylamine | 109-28-4 |
| N-3-Erucylamidopropyl dimethylamine | 60270-33-9 |
| N-Oleyl 1,3-propanediamine | 7173-62-8 |
| Bis(aminopropyl)laurylamine | 2372-82-9 |
| N-tallow alkyltripropylenetetra | 68911-79-5 |
| 3-(isodecyloxy)propylamine | 30113-45-2 |
| N-[3-(isodecyloxy)propyl]propane-1,3-diamine | 72162-46-0 |
| 2-(Methylamino)ethanol | 109-83-1 |
| N-Methyldiethanolamine | 105-59-9 |
| 3-Methoxy propyl amine | 5332-73-0 |
| N,N-dimethylcyclohexylamine | 98-94-2 |
| 1,3,5-Tris[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]hexahydro-1,3,5-triazine | 15875-13-5 |
| N,N,N’-trimethylamino-N’-ethylethanolamine | 2212-32-0 |
| N,N-Dimethylethanolamine | 108-01-1 |
| Acetone | |
| Acrylic acid | |
| Adipic acid | |
| Alpha-Methylstyrene (AMS) | |
| Benzoic Acid | |
| Bisphenol A | |
| Butyl Acrylat (BA) | |
| Butyl acetate (Butac) | |
| Butyl diglycol (BDG) | |
| Butyl glycol | |
| Para-tertiary butyl benzoic acid (PTBBA) | |
| n-Butanol | |
| n-Butyl methacrylate (n-BUMA) | |
| para-tert. Butylphenol (PTBP) | |