product description
Basic Info.
Dipropylamine Properties
| Melting point | -63 °C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 105-110 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.738 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 38 hPa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | n20/D 1.4049(lit.) |
| Flash point | 39 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 35g/l (experimental) |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | pK1:10.91(+1) (25°C) |
| color | Clear |
| explosive limit | 1.8-9.3%(V) |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Merck | 14,3343 |
| BRN | 505974 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.9(21℃) |
| Stability | Stable. Highly flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| InChI | 1S/C6H15N/c1-3-5-7-6-4-2/h7H,3-6H2,1-2H3 |
| InChIKey | WEHWNAOGRSTTBQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
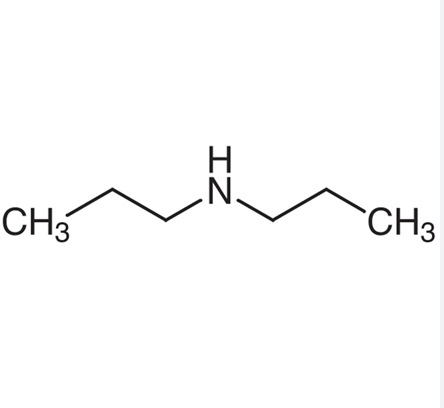
| SMILES | CCCNCCC |
| LogP | 1.33 at 23℃ |
| Dissociation constant | 11 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 142-84-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EWG’s Food Scores | 1 |
| FDA UNII | 60P318IIRY |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1-Propanamine, n-propyl-(142-84-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Dipropylamine (142-84-7) |
| UNSPSC Code | 12352116 |
| NACRES | NA.22 |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS02,GHS05,GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H225-H302-H311+H331-H314-H335 |
| Precautionary statements | P210-P280-P301+P312-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340+P310-P305+P351+P338 |
| target organs | Respiratory system |
| PPE | Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | F,C |
| Risk Statements | 11-20/21/22-35 |
| Safety Statements | 16-26-36/37/39-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2383 3/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | JL9200000 |
| Autoignition Temperature | 260 °C |
| TSCA | TSCA listed |
| HazardClass | 3 |
| PackingGroup | II |
| HS Code | 29211910 |
| Storage Class | 3 – Flammable liquids |
| Hazard Classifications | Acute Tox. 3 Dermal Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation Acute Tox. 4 Oral Eye Dam. 1 Flam. Liq. 2 Skin Corr. 1A STOT SE 3 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 142-84-7(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 0.93 g/kg, H. F. Smyth et al., Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 23, 95 (1962) |
| Limited Quantities | 1.0 L (0.3 gallon) (liquid) |
| Excepted Quantities | Max Inner Pack (30g or 30ml) and Max Outer Pack (500g or 500ml) |
Dipropylamine Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Dipropylamine is a colorless, water-white liquid with a strong ammonia-like odor. Molecularweight= 101.22; Boiling point = 110℃; Freezing/Meltingpoint = 263℃; Vapor pressure= 29.8 mmHg at 25℃;Flash point = 17℃; Autoignition temperature= 299℃.Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 M RatingSystem): Health 3, Flammability 4, Reactivity 1. Insolublein water
Chemical Properties
colourless liquid
Chemical Properties
Dipropylamine, like the other short chain aliphatic amines, is a very strong base, its reactivity being governed by the unshared electron pair on the nitrogen atom. It forms a hydrate with water. The amine also can react with inorganic or organic nitrites under acidic conditions and possibly by reaction with nitrogen oxides from the air to form the highly mutagenic and carcinogenic N-nitrosodipropylamine (ATSDR 1979; Olah et al; Scanlan 1983).
Uses
n-Dipropylamine is a useful reagent for the preparation of perylene derivatives for photosensitive fluorescent resins.
Production Methods
Dipropylamine is manufactured by reaction of propanol and ammonia over a dehydration catalyst at high temperature and pressure (HSDB 1989). Alternatively, propanol and ammonia can be combined with hydrogen over a dehydrogenation catalyst. In each instance, the resulting mixture of primary, secondary, and tertiary amines can be separated by continuous distillation and extraction (Schweizer et al 1978). Dipropylamine is a natural component of vegetables, fish, fruits, and other foods (Mohri 1987) and of tobacco products (WHO 1987). It also is found in human urine (Audunsson 1988), waste water lagoons (Guzewich et al 1983) and in workplace air (Simon and Lemacon 1987).
The toxic compound, N-nitrosodipropylamine, can be produced inadvertently by nitrosation of n-dipropylamine during various manufacturing processes that use the diamine (ATSDR 1989). The nitrosamine, therefore, occurs as an impurity in some dinitroaniline pesticides and rubber products. N-nitrosodipropylamine also is found in various foodstuffs including cheese, cured meats, cooked fish and alcoholic beverages, apparently by reaction of n-dipropylamine with the preservative sodium nitrite (ATSDR 1979; Gross and Newberne 1977; Scanlan 1983).
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Flash point 30°F. Less dense than water. Vapors heavier than air. Toxic oxides of nitrogen produced during combustion.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Dipropylamine neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen may be generated in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides.
Health Hazard
Inhalation causes severe coughing and chest pain due to irritation of air passages; can-cause lung edema; may also cause headache, nausea, faintness, and anxiety. Ingestion causes irritation and burning of mouth and stomach. Contact with eyes causes severe irritation and edema of the cornea. Contact with skin causes severe irritation.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of dipropylamine vapors can result in severe coughing and chest pain due to irritation of airways. Transient symptoms of exposure may include headache, nausea, faintness, and anxiety. Prolonged breathing of vapors may result in lung edema. Dipropylamine also can cause severe irritation and edema of the cornea. A review of the toxicity of dipropylamine has been prepared (Anon 1987).
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic oxides of nitrogen may form in fires.
Industrial uses
Dipropylamine is used in the rubber industry and as a chemical intermediate in the manufacture of the herbicides S-ethyl-di-n-propylthiocarbamate and S-propyl di-n-propylthiocarbamate (HSDB 1989). Dipropylamine also is employed in the purification of perfluoro compounds to convert the incompletely fluorinated impurities to solids which are then removed by filtration. In 1984, U.S. production was 41 million pounds.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion. Moderately toxic by shin contact and inhalation. A skin irritant. A very dangerous fire hazard, when exposed to heat or flame. Can react with oxidizers. Explosion hazard is unknown. Keep away from heat and open flame. To fight fire, use foam, CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx,. See also AMINES
Potential Exposure
Used as a chemical intermediate andin the manufacture of herbicides.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. If victim is conscious, administer water ormilk. Do not induce vomiting. Medical observation isrecommended for 2448 h after breathing overexposure, aspulmonary edema may be delayed. As first aid for pulmonary edema, a doctor or authorized paramedic may consideradministering a corticosteroid spray.
Metabolism
There is little information available on the metabolism and disposition of dipropylamine in biological systems. The available evidence suggests that dipropylamine is not a substrate for monoamine oxidase, but rather is inhibitory. Valiev (1974) administered dipropylamine intraperitoneally to rats and reported it to be moderately inhibitory to liver monoamine oxidase. Previous work by this author demonstrated that lethal doses of dipropylamine and other secondary and tertiary amines significantly inhibited rat liver monoamine oxidase activity (Valiev 1968).
The carcinogenic N-nitrosodipropylamine has been detected in the stomach when dipropylamine (present in fish, vegetables and fruit juices) comes in contact with nitrite, which is often used as a food additive in meats and smoked fish (HSDB 1989). Further metabolism of the carcinogen N-nitrosodipropylamine product formed upon nitrosation of dipropylamine is required to form a highly electrophilic carbonium ion capable of alkylating DNA, etc. (Archer 1981).
storage
Color Code—Red: Flammability Hazard: Store ina flammable liquid storage area or approved cabinet awayfrom ignition sources and corrosive and reactive materials.Prior to working with dipropylamine you should be trainedon its proper handling and storage. Before entering confined space where this chemical may be present, check tomake sure that an explosive concentration does not exist.Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilatedarea. Metal containers involving the transfer of this chemical should be grounded and bonded. Where possible, automatically pump liquid from drums or other storagecontainers to process containers. Drums must be equippedwith self-closing valves, pressure vacuum bungs, andflame arresters. Use only nonsparking tools and equipment, especially when opening and closing containers ofthis chemical. Sources of ignition, such as smoking andopen flames, are prohibited where this chemical is used,handled, or stored in a manner that could create a potential fire or explosion hazard. Wherever this chemical isused, handled, manufactured, or stored, use explosionproof electrical equipment and fittings.
Shipping
This compound requires a shipping label of“FLAMMABLE LIQUID, CORROSIVE.” It falls intoHazard Class 3 and Packing Group II
Incompatibilities
Forms explosive mixture with air.Incompatible with acids, organic anhydrides, isocyanates,vinyl acetate, acrylates, substituted allyls, alkylene oxides,epichlorohydrin, ketones, aldehydes, alcohols, glycols, mercury, phenols, cresols, caprolactum solution, strong oxidizers. Attacks aluminum, copper, lead, tin, zinc, and theiralloys
Toxics Screening Level
The Initial Threshold Screening Level (ITSL) for Di-n-propylamine is 1.5 μg/m3 based on annual averaging time.
Dipropylamine Preparation Products And Raw materials
FAQ
Q1: About the after-sale service of products
A: After purchasing the products from our factory, we have A professional technical team and after-sales team to serve you and solve all your problems in the future.
Q2: Can I get some samples?
A: Yes, we can provide samples, but the customer will pay the freight.
Q3: How do I start paying?
Payment can be made by wire transfer or T/T, apple_pay, google_pay, gc_real_time_bank_transfer , etc.
Q4: How to confirm product quality before placing an order?
A: You can get free samples of some products. You just have to pay the shipping fee or arrange for the sample to be sent to us by express.
You can send us your product specifications and requirements and we will produce products according to your requirements.
Q5: What is your MOQ?
A: The minimum quantity we can order is 1kg.
But usually we can accept a smaller quantity, say 100g, at the cost of 100% sample charge.
Q6: Shipping Time?
A: We ship the parcel out in 1-2 days and offer tracking No.. Shipping time is different to different country. Please consult
| ACF Chemical Co., Ltd.
Leon phone/whatsapp:008615950692266 email:md@acfchemical.com No. 45 Pengwan Road, Qianwan Bonded Port Area, Qingdao Area, China (Shandong) |
|
| DMEA | 108-01-0 |
| Dodecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride | 112-00-5 |
| N-Hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride | 112-02-7 |
| 1831 | 112-03-8 |
| 1631Br | 57-09-0 |
| D821 | 5538-94-3 |
| D8/1021 | 68424-95-3 |
| D1021 | 7173-51-5 |
| D1821 | 61789-80-8 |
| TEP88 | 157905-74-3 |
| 1227 C12 | 139-07-1 |
| DMPT(N,N-Dimethyl-p-toluidine) | 99-97-8 |
| NDPT(N,N-dihydroxyethyl-p-toluidine) | 3077-12-1. |
| DMA(N,N-dimethylaniline) | 121-69-7 |
| N,N-Diethylaniline | 91-66-7 |
| MT(M-Toluidine) | 108-44-1 |
| PT(P-Toluidine) | 106-49-0 |
| O-Toluidine OT | 95-53-4 |
| Dimethyl(octyl)amine | 7378-99-6/1120-24-7 |
| C16-18-alkyldimethyl Octadecyl/Hexadecyl dimethylamines | 68390-97-6 |
| Octadecyl/behenyl dimethylamines | 124046-42-0 |
| N,N-dimethyldocosylamine | 21542-96-1 |
| N-Methyldioctylamine | 4455-26-9 |
| Di(octyl/decyl) methylamines | 308062-61-5 |
| Didecyl methylamine | 7396-58-9 |
| N-methyldidodecylamine | 2915-90-4 |
| Dipalmitamine | 16724-61-1 |
| Trioctylamine | 1116-76-3 |
| Trioctylamine | 68814-95-9 |
| N-3-Laurylamidopropyl dimethylamine | 3179-80-4 |
| N-3-(Hydrogenated cocoamido)propyl dimethylamines | 288095-05-6 |
| N-3-Oleylamidopropyl dimethylamine | 109-28-4 |
| N-3-Erucylamidopropyl dimethylamine | 60270-33-9 |
| N-Oleyl 1,3-propanediamine | 7173-62-8 |
| Bis(aminopropyl)laurylamine | 2372-82-9 |
| N-tallow alkyltripropylenetetra | 68911-79-5 |
| 3-(isodecyloxy)propylamine | 30113-45-2 |
| N-[3-(isodecyloxy)propyl]propane-1,3-diamine | 72162-46-0 |
| 2-(Methylamino)ethanol | 109-83-1 |
| N-Methyldiethanolamine | 105-59-9 |
| 3-Methoxy propyl amine | 5332-73-0 |
| N,N-dimethylcyclohexylamine | 98-94-2 |
| 1,3,5-Tris[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]hexahydro-1,3,5-triazine | 15875-13-5 |
| N,N,N’-trimethylamino-N’-ethylethanolamine | 2212-32-0 |
| N,N-Dimethylethanolamine | 108-01-1 |
| Acetone | |
| Acrylic acid | |
| Adipic acid | |
| Alpha-Methylstyrene (AMS) | |
| Benzoic Acid | |
| Bisphenol A | |
| Butyl Acrylat (BA) | |
| Butyl acetate (Butac) | |
| Butyl diglycol (BDG) | |
| Butyl glycol | |
| Para-tertiary butyl benzoic acid (PTBBA) | |
| n-Butanol | |
| n-Butyl methacrylate (n-BUMA) | |
| para-tert. Butylphenol (PTBP) | |