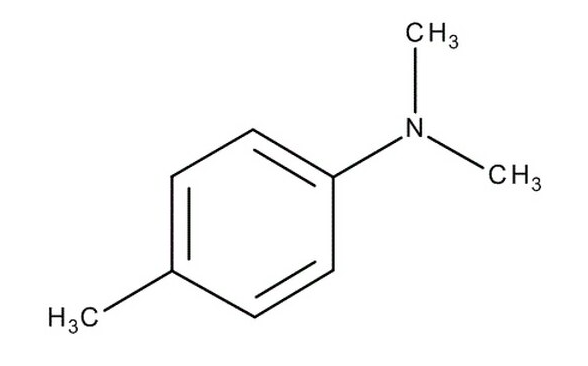
N,N-Dimethyl-p-toluidine CAS Number: 99-97-8
| Product | N,N-Dimethyl-p-toluidine |
| CAS | 99-97-8 |
| Formula | C9H13N |
| Synonym | N,N,4-TRIMETHYLBENZENAMINE;N,N-DIMETHYL-4-METHYLANILINE;N,N-DIMETHYL-4-TOLUIDINE;N,N-DIMETHYL-PARA-TOLChemicalbookUIDINE;N,N-DIMETHYL-P-TOLUIDINE;Benzeneamine,N,N,4-trimethyl-;dimethyl-4-toluidine;Dimethyl-p-toluidine |
product description
Properties, Uses, and Production Process of N,N-Dimethyl-p-Toluidine
| Description | |
|---|---|
| Catalogue Number | 822040 |
| Synonyms | 4-Dimethylaminotoluene |
| Description | N,N-Dimethyl-p-toluidine |
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| CAS number | 99-97-8 |
| EC index number | 612-056-00-9 |
| EC number | 202-805-4 |
| Hill Formula | C₉H₁₃N |
| Chemical formula | 4-(CH₃)C₆H₄N(CH₃)₂ |
| Molar Mass | 135.21 g/mol |
| HS Code | 2921 43 29 |
| Structure formula Image | |
| Quality Level | MQ200 |
| Applications | |
|---|---|
| Application | N,N-Dimethyl-p-toluidine for synthesis. CAS 99-97-8, EC Number 202-805-4, chemical formula 4-(CH₃)C₆H₄N(CH₃)₂. |
| Toxicological Information | |
|---|---|
| LD 50 oral | LD50 Rat 1650 mg/kg |
| Safety Information | |
|---|---|
| Categories of danger | toxic, dangerous for the environment |
| Storage and Shipping Information | |
|---|---|
| Storage | Store below +30°C. |
| Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Color according to color reference solution Ph.Eur. | not more intensely colored than Y3 |
| Assay (GC, area%) | ≥ 98.0 % (a/a) |
| Density (d 20 °C/ 4 °C) | 0.935 – 0.937 |
| Identity (IR) | passes test |
**Physicochemical Properties:**
N,N-Dimethyl-p-toluidine is a colorless or pale yellow oily liquid with a rotten egg odor. It has a melting point of 130.31℃, a boiling point of 211.5-212.5℃, a density of 0.9287-0.9366 g/mL at room temperature, and a refractive index of 1.5360-1.5470. It is insoluble in water but soluble in some organic solvents, and decomposes upon exposure to light.
**Product Description:**
N,N-Dimethyl-p-toluidine is soluble in some organic solvents and decomposes upon exposure to light. It is an effective photoinitiator for acrylonitrile (AN) polymerization and can also be used in the production of self-curing dental adhesive.
**Polymerization Reaction:**
Aromatic tertiary amines, especially N,N-dimethyl-p-toluidine, are effective photoinitiators for acrylonitrile (AN) polymerization. The medium has a significant impact on the polymerization rate; a polarity results in a faster polymerization rate. Oxygen has a significant effect on polymerization; as the oxygen content increases, the polymerization induction period increases, and the polymerization rate decreases. N,N-Dimethyl-p-toluidine is generally considered a retarder for olefin polymerization, not an initiator for the photopolymerization of acrylonitrile (AN).
Polymerization Characteristics:
N,N-Dimethyl-p-toluidine cannot initiate the polymerization of acrylonitrile (AN) in the dark, but it initiates polymerization extremely rapidly under light. Figure 1 shows the photopolymerization of acrylonitrile (AN) in the presence of N,N-dimethyl-p-toluidine, naphthalene, benzophenone (BP)-triethylamine (TEA), and AClN, with polymerization rates of 0.157, 0.023, 0.139, and 0.045% min⁻¹, respectively, indicating that N,N-dimethyl-p-toluidine is a highly effective initiator for the photopolymerization of acrylonitrile (AN).
The photopolymerization of acrylonitrile (AN) initiated by N,N-dimethyl-p-toluidine proceeds via a free radical mechanism. The polymerization completely stops upon the addition of a trace amount of free radical scavenger. For example, [N,N-dimethyl-p-toluidine]-10-3M, when 200 ppm of 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinol nitroxide free radicals are added, shows no polymerization of acrylonitrile (AN) after 1.5 hours of light irradiation. However, under the same conditions without a free radical scavenger, a white precipitate of polyacrylonitrile appears within two minutes.
Applications:
As an effective photoinitiator for acrylonitrile (AN) polymerization, its polymerization rate is directly proportional to the 1.62 power of the AN concentration and the 0.62 power of the DMT concentration. This product is commonly used as an accelerator and can also be used in the synthesis of unsaturated polyesters and as an additive in adhesives.
Synthesis Method:
N,N-dimethyl-p-toluidine is synthesized at low temperature and ambient pressure using dimethyl sulfate as a methylating agent.
Uses
Used in the manufacture of self-curing dental trays
Uses
A tertiary amine that can undergo iron-catalyzed oxidative C-C coupling with phenylacetylene and benzamide in the presence of di-tert-butyl peroxide to form N,4-dimethyl-N-(3-phenylprop-2-ynyl)benzamide and N-((methyl(p-tolyl)amino)methyl)benzamide, respectively.
| ACF Chemical Co., Ltd. Leon : phone/whatsapp:008615950692266 email:md@acfchemical.com No. 45 Pengwan Road, Qianwan Bonded Port Area, Qingdao Area, China (Shandong) welcome to vist our factory. sample is free ACF Chemical Qingdao Co., Ltd. was established in 1987. the company has over decades of experience in the production of methacrylate and acrylate series products, as well as high-efficiency polymerization inhibitors and rubber and plastic antioxidant series products. The company’s leading products are high-efficiency polymerization inhibitor series products, with an annual production capacity of 1,000 tons of tert-butylhydroquinone (TBC), 800 tons of polymerization inhibitor TH-701, 500 tons of polymerization inhibitor TH-A294, 500 tons of polymerization inhibitor TH-100BE, 500 tons of phenothiazine, and 200 tons of hydroquinone. |
|
| DMEA | 108-01-0 |
| Dodecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride | 112-00-5 |
| N-Hexadecyltrimethylammonium chloride | 112-02-7 |
| 1831 | 112-03-8 |
| 1631Br | 57-09-0 |
| D821 | 5538-94-3 |
| D8/1021 | 68424-95-3 |
| D1021 | 7173-51-5 |
| D1821 | 61789-80-8 |
| TEP88 | 157905-74-3 |
| 1227 C12 | 139-07-1 |
| DMPT(N,N-Dimethyl-p-toluidine) | 99-97-8 |
| NDPT(N,N-dihydroxyethyl-p-toluidine) | 3077-12-1. |
| DMA(N,N-dimethylaniline) | 121-69-7 |
| N,N-Diethylaniline | 91-66-7 |
| MT(M-Toluidine) | 108-44-1 |
| PT(P-Toluidine) | 106-49-0 |
| O-Toluidine OT | 95-53-4 |
| Dimethyl(octyl)amine | 7378-99-6/1120-24-7 |
| C16-18-alkyldimethyl Octadecyl/Hexadecyl dimethylamines | 68390-97-6 |
| Octadecyl/behenyl dimethylamines | 124046-42-0 |
| N,N-dimethyldocosylamine | 21542-96-1 |
| N-Methyldioctylamine | 4455-26-9 |
| Di(octyl/decyl) methylamines | 308062-61-5 |
| Didecyl methylamine | 7396-58-9 |
| N-methyldidodecylamine | 2915-90-4 |
| Dipalmitamine | 16724-61-1 |
| Trioctylamine | 1116-76-3 |
| Trioctylamine | 68814-95-9 |
| N-3-Laurylamidopropyl dimethylamine | 3179-80-4 |
| N-3-(Hydrogenated cocoamido)propyl dimethylamines | 288095-05-6 |
| N-3-Oleylamidopropyl dimethylamine | 109-28-4 |
| N-3-Erucylamidopropyl dimethylamine | 60270-33-9 |
| N-Oleyl 1,3-propanediamine | 7173-62-8 |
| Bis(aminopropyl)laurylamine | 2372-82-9 |
| N-tallow alkyltripropylenetetra | 68911-79-5 |
| 3-(isodecyloxy)propylamine | 30113-45-2 |
| N-[3-(isodecyloxy)propyl]propane-1,3-diamine | 72162-46-0 |
| 2-(Methylamino)ethanol | 109-83-1 |
| N-Methyldiethanolamine | 105-59-9 |
| 3-Methoxy propyl amine | 5332-73-0 |
| N,N-dimethylcyclohexylamine | 98-94-2 |
| 1,3,5-Tris[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]hexahydro-1,3,5-triazine | 15875-13-5 |
| N,N,N’-trimethylamino-N’-ethylethanolamine | 2212-32-0 |
| N,N-Dimethylethanolamine | 108-01-1 |
| Acetone | |
| Acrylic acid | |
| Adipic acid | |
| Alpha-Methylstyrene (AMS) | |
| Benzoic Acid | |
| Bisphenol A | |
| Butyl Acrylat (BA) | |
| Butyl acetate (Butac) | |
| Butyl diglycol (BDG) | |
| Butyl glycol | |
| Para-tertiary butyl benzoic acid (PTBBA) | |
| n-Butanol | |
| n-Butyl methacrylate (n-BUMA) | |
| para-tert. Butylphenol (PTBP) | |